Description
Șimleu Silvaniei Smart Specialization Park is an innovative initiative developed by the Șimleu Silvaniei Municipality, aiming to foster sustainable economic growth and support innovation at the regional level.
The project is financed through the North-West Regional Programme 2021–2027, with a total of EUR 1.5 million allocated for the development of modern and functional infrastructure. Additionally, a pre-allocated budget of EUR 4 million is available to resident small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), providing substantial financial support for their growth and development.
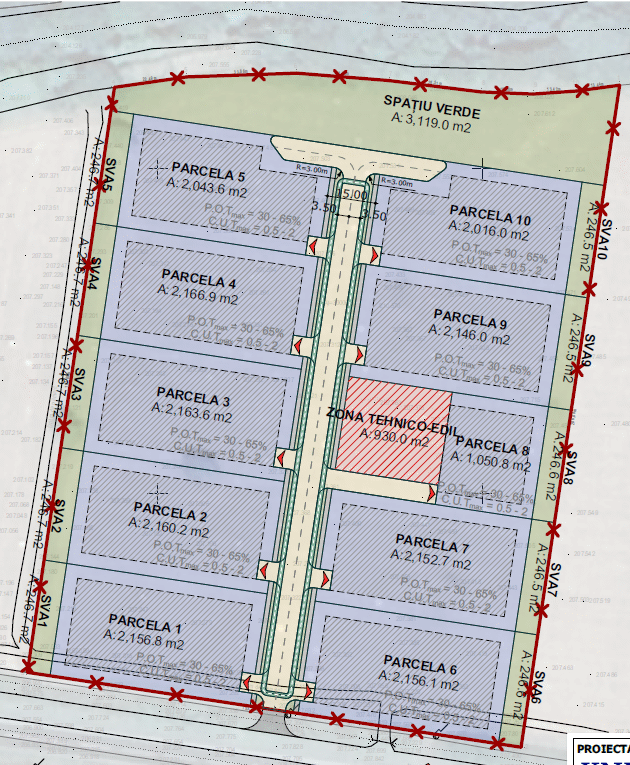
The park is located in Sălaj County, in the city of Șimleu Silvaniei, on Tudor Vladimirescu Street, on a 30,000 m² urban plot owned by the project’s founder. The area is currently undeveloped, and the available investment plots range between 1,050.77 m² and 2,166.91 m², allowing for flexibility according to investors’ specific needs.
- Project name: Șimleu Silvaniei Smart Specialization Park
- Location: Eastern part of Șimleu Silvaniei
View on Google Maps - Total area: 30,000 m² (10 plots)
- Contract type: Concession
- Owner: Șimleu Silvaniei Municipality
- Park Administrator: Company established by the Șimleu Silvaniei Municipality
The residents of the smart specialization park will benefit from all necessary utilities.
- Internal roads with public lighting
- Utility networks: water, sewage, electricity, gas
- Advanced telecom network with fiber optic high-speed internet
- Electric vehicle charging stations (sustainable mobility)
- Green energy and energy efficiency infrastructure:
- Solar panels for public lighting
- Dry boreholes for heat pump systems
Proximity to Major Cities:
- Zalău: 25 km
- Cluj-Napoca: 110 km
- Oradea: 95 km
- Budapest: 355 km
European Roads:
- E81 – 16 km
Highways:
- Transylvania Motorway (Nușfalău exit) – 14 km
Border Crossing Points:
- Ukraine (Borș): 101 km
Seaports:
- Constanța (Romania) – 780 km
- Koper (Slovenia) – 944 km
International Airports:
- Cluj-Napoca International Airport (Avram Iancu) – 118 km
- Satu Mare International Airport – 70 km
- Oradea International Airport – 97 km
- Maramureș International Airport – 104 km
Investors will benefit from significant tax incentives, including:
- 100% deduction of profits reinvested for development purposes, as defined by current legislation, when calculating taxable profits for companies investing within the smart specialization park.
- 50% deduction from taxable profits for investments made by the park administrator in building, refurbishing, or connecting the park to public utilities, in accordance with applicable legal standards for asset classification and depreciation.
- 100% deduction from taxable profits for economic operators who have signed concession or administration contracts and make investments in buildings or equipment dedicated to smart specialization activities, subject to legal norms for asset classification and useful life.
Reduction of concession fees—by up to 50%—for companies that have invested in the smart specialization park, based on a decision by the local council.
The Smart Specialization Park is managed by a legally established entity designated by the park’s founders, in accordance with Article 40 of Government Emergency Ordinance (GEO) no. 112/2022. The administrator is responsible for overseeing and coordinating the park’s operations. Key responsibilities include:
- Managing buildings and utility infrastructure;
- Providing essential services to park residents based on contractual agreements;
- Ensuring efficient use of infrastructure and utilities;
- Carrying out repairs, maintenance, modernization, and further development of infrastructure as needed;
- Coordinating with utility service providers to ensure uninterrupted functionality when infrastructure is externally managed;
- Managing both own and attracted financial resources in line with the park’s development plan.
The project is supported by a cluster and a digital innovation hub, both of which have issued letters of endorsement. These organizations actively contribute to the project by delivering specialized services aimed at facilitating the transfer of research, knowledge, and innovation capacity. Services include:
- Technological assistance for innovation processes
- Consultancy and expertise for validating ideas and solutions (including business diagnostics to identify the most appropriate innovative technical solutions)
- Support for securing, protecting, and commercializing industrial property rights
- Support for product, service, and process certification, standardization, and compliance
Construction Regulations
- Maximum Plot Occupation: 60%
- Maximum Building Density: 2
- Maximum Building Height: P+1E
- Annexes: allowed
- Project name: Șimleu Silvaniei Smart Specialization Park
- Location: Eastern part of Șimleu Silvaniei
View on Google Maps - Total area: 30,000 m² (10 plots)
- Contract type: Concession
- Owner: Șimleu Silvaniei Municipality
- Park Administrator: Company established by the Șimleu Silvaniei Municipality
The residents of the smart specialization park will benefit from all necessary utilities.
- Internal roads with public lighting
- Utility networks: water, sewage, electricity, gas
- Advanced telecom network with fiber optic high-speed internet
- Electric vehicle charging stations (sustainable mobility)
- Green energy and energy efficiency infrastructure:
- Solar panels for public lighting
- Dry boreholes for heat pump systems
Proximity to Major Cities:
- Zalău: 25 km
- Cluj-Napoca: 110 km
- Oradea: 95 km
- Budapest: 355 km
European Roads:
- E81 – 16 km
Highways:
- Transylvania Motorway (Nușfalău exit) – 14 km
Border Crossing Points:
- Ukraine (Borș): 101 km
Seaports:
- Constanța (Romania) – 780 km
- Koper (Slovenia) – 944 km
International Airports:
- Cluj-Napoca International Airport (Avram Iancu) – 118 km
- Satu Mare International Airport – 70 km
- Oradea International Airport – 97 km
- Maramureș International Airport – 104 km
Investors will benefit from significant tax incentives, including:
- 100% deduction of profits reinvested for development purposes, as defined by current legislation, when calculating taxable profits for companies investing within the smart specialization park.
- 50% deduction from taxable profits for investments made by the park administrator in building, refurbishing, or connecting the park to public utilities, in accordance with applicable legal standards for asset classification and depreciation.
- 100% deduction from taxable profits for economic operators who have signed concession or administration contracts and make investments in buildings or equipment dedicated to smart specialization activities, subject to legal norms for asset classification and useful life.
Reduction of concession fees—by up to 50%—for companies that have invested in the smart specialization park, based on a decision by the local council.
The Smart Specialization Park is managed by a legally established entity designated by the park’s founders, in accordance with Article 40 of Government Emergency Ordinance (GEO) no. 112/2022. The administrator is responsible for overseeing and coordinating the park’s operations. Key responsibilities include:
- Managing buildings and utility infrastructure;
- Providing essential services to park residents based on contractual agreements;
- Ensuring efficient use of infrastructure and utilities;
- Carrying out repairs, maintenance, modernization, and further development of infrastructure as needed;
- Coordinating with utility service providers to ensure uninterrupted functionality when infrastructure is externally managed;
- Managing both own and attracted financial resources in line with the park’s development plan.
The project is supported by a cluster and a digital innovation hub, both of which have issued letters of endorsement. These organizations actively contribute to the project by delivering specialized services aimed at facilitating the transfer of research, knowledge, and innovation capacity. Services include:
- Technological assistance for innovation processes
- Consultancy and expertise for validating ideas and solutions (including business diagnostics to identify the most appropriate innovative technical solutions)
- Support for securing, protecting, and commercializing industrial property rights
- Support for product, service, and process certification, standardization, and compliance
Construction Regulations
- Maximum Plot Occupation: 60%
- Maximum Building Density: 2
- Maximum Building Height: P+1E
- Annexes: allowed
Galerie